The Virtual Evolution Stickleback Lab, an innovative platform, invites researchers and enthusiasts alike to delve into the captivating world of evolutionary biology. This virtual laboratory provides an unparalleled opportunity to witness the transformative power of evolution in action, offering insights into the remarkable adaptations of stickleback species.
Through the lens of the Virtual Evolution Stickleback Lab, we embark on a journey to explore the genetic mechanisms underlying stickleback evolution, unraveling the intricate interplay between genetic variations and environmental pressures. This immersive experience empowers us to manipulate genetic traits and environmental conditions, gaining valuable insights into the evolutionary processes that have shaped the diversity of life on Earth.
1. Stickleback Species and Habitat
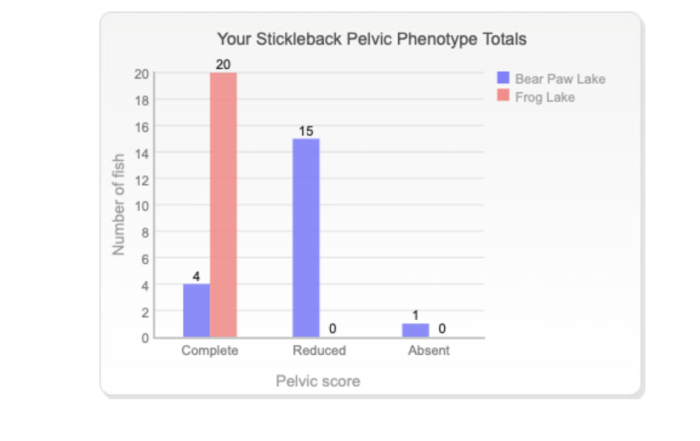
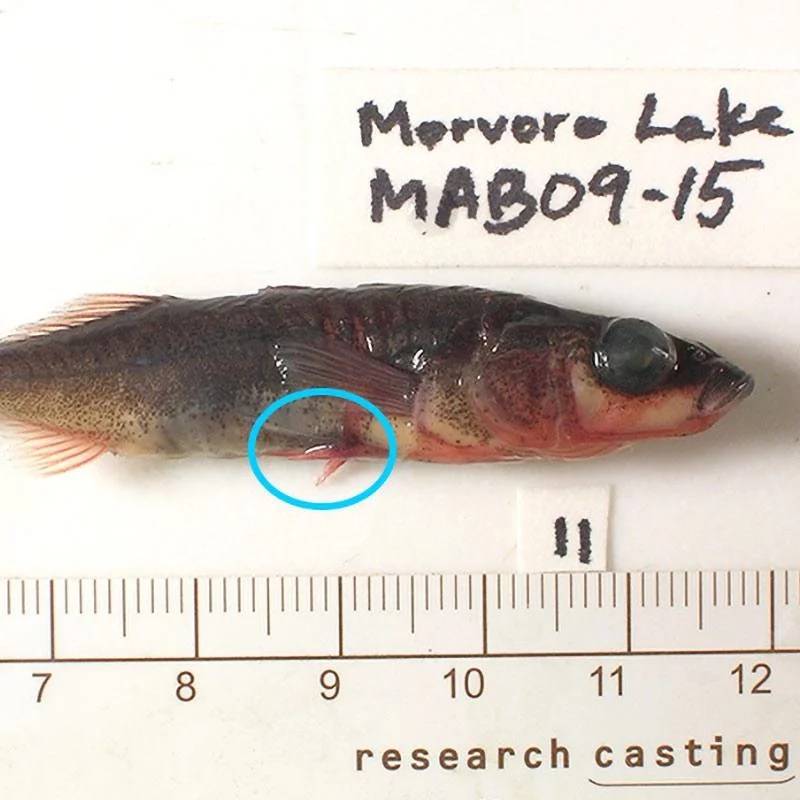
Sticklebacks, small and spiny-rayed fish, exhibit remarkable diversity in body form and ecological adaptations. They inhabit a wide range of environments, including freshwater lakes, streams, estuaries, and marine coastal waters. Three-spine sticklebacks (Gasterosteus aculeatus) have colonized isolated lakes in British Columbia and undergone rapid evolution, providing a unique opportunity to study speciation and adaptive radiation.
Unique Adaptations and Habitat Preferences
- Freshwater sticklebacks:Possess reduced armor plates and longer pelvic fins for swimming in slow-moving waters, and feed on insects and small crustaceans.
- Marine sticklebacks:Have larger armor plates and shorter pelvic fins, enabling them to withstand stronger water currents and waves, and prey on zooplankton and small fish.
- Estuarine sticklebacks:Show intermediate characteristics, adapting to both freshwater and saltwater environments, and feeding on a variety of prey.
Factors Influencing Stickleback Evolution and Speciation
- Geographic isolation:Isolated populations experience different selective pressures, leading to genetic divergence and the formation of new species.
- Predation pressure:Predators such as birds and fish can exert strong selection on stickleback body size, armor, and coloration.
- Resource competition:Competition for food and mates can drive the evolution of different feeding strategies and reproductive behaviors.
2. Virtual Evolution Stickleback Lab

The Virtual Evolution Stickleback Lab is an online simulation that models the evolution of sticklebacks in a virtual environment. It allows researchers to manipulate genetic traits, environmental conditions, and observe the resulting evolutionary changes over generations.
Simulation Design and Genetic Manipulation
- Virtual population:The lab creates a virtual population of sticklebacks with varying genetic traits, such as body size, armor plates, and feeding preferences.
- Genetic mutations:Researchers can introduce genetic mutations into the population, simulating natural genetic variation.
- Selection pressures:The lab allows for the manipulation of environmental conditions, such as predation pressure, resource availability, and habitat type.
Advantages and Limitations of Virtual Labs
- Advantages:
- Allows for controlled experiments with high replication.
- Provides a safe and ethical environment for studying evolution.
- Can simulate long-term evolutionary processes in a relatively short time.
- Limitations:
- May not fully capture the complexity of real-world ecosystems.
- Relies on assumptions and simplifications.
- Cannot replace field studies or direct observations.
3. Experimental Design and Procedures
The Virtual Evolution Stickleback Lab employs a controlled experimental design to study the effects of genetic variations and environmental changes on stickleback evolution.
Experimental Setup
- Treatment groups:Researchers create multiple treatment groups, each with different combinations of genetic traits and environmental conditions.
- Control groups:Control groups are established to provide a baseline for comparison.
- Multiple generations:The lab simulates multiple generations of sticklebacks, allowing for the accumulation of genetic changes and the observation of evolutionary trends.
Data Collection and Analysis
- Trait measurements:Researchers collect data on various stickleback traits, such as body size, armor plates, and feeding preferences.
- Genetic analysis:The lab tracks genetic changes in the population over time, identifying the effects of specific mutations.
- Statistical analysis:Statistical methods are used to analyze the data, identifying significant differences between treatment and control groups, and testing hypotheses about the effects of genetic variations and environmental conditions.
4. Evolutionary Patterns and Trends: The Virtual Evolution Stickleback Lab

The Virtual Evolution Stickleback Lab has revealed several key evolutionary patterns and trends in stickleback populations.
Genetic Variation and Adaptation
- Genetic variation is essential for evolution, providing the raw material for natural selection to act upon.
- In the lab, stickleback populations with higher genetic variation adapt more rapidly to changing environmental conditions.
Effects of Environmental Changes
- Environmental changes can exert strong selective pressures on stickleback populations.
- For example, increased predation pressure favors the evolution of larger armor plates, while increased resource competition promotes the evolution of smaller body size.
Coevolution and Species Interactions
- The lab allows for the simulation of coevolutionary interactions between sticklebacks and their predators and competitors.
- Coevolutionary processes can lead to the emergence of complex adaptations and ecological relationships.
5. Applications and Future Directions
The Virtual Evolution Stickleback Lab has a wide range of potential applications and future research directions.
Educational and Outreach, The virtual evolution stickleback lab
- The lab serves as an educational tool for teaching evolutionary principles and concepts.
- It can be used to engage students in hands-on simulations and foster scientific inquiry.
Research and Conservation
- The lab can provide insights into the evolutionary processes that drive species diversification and adaptation.
- It can aid in the conservation of endangered species by identifying the genetic and environmental factors that influence their survival.
Future Advancements
- Future research directions include incorporating more realistic ecological interactions and environmental complexity into the lab.
- Advances in computational power will enable the simulation of larger populations and longer evolutionary timescales.
Essential Questionnaire
What is the Virtual Evolution Stickleback Lab?
The Virtual Evolution Stickleback Lab is an online platform that simulates stickleback evolution, allowing researchers to study genetic changes and their impact on adaptation.
Why are sticklebacks a good model for studying evolution?
Sticklebacks have a short generation time and a wide range of habitats, making them an ideal species for studying evolutionary changes over multiple generations.
What are the advantages of using a virtual lab to study evolution?
Virtual labs provide a controlled environment for studying evolution, allowing researchers to manipulate genetic traits and environmental conditions without the limitations of real-world experiments.
What are the limitations of using a virtual lab to study evolution?
Virtual labs cannot fully replicate the complexity of real-world environments, and the results obtained may not always be directly applicable to natural populations.
How can the Virtual Evolution Stickleback Lab be used in education and outreach?
The Virtual Evolution Stickleback Lab can be used as a teaching tool to demonstrate evolutionary principles and as a platform for engaging the public in discussions about evolution.